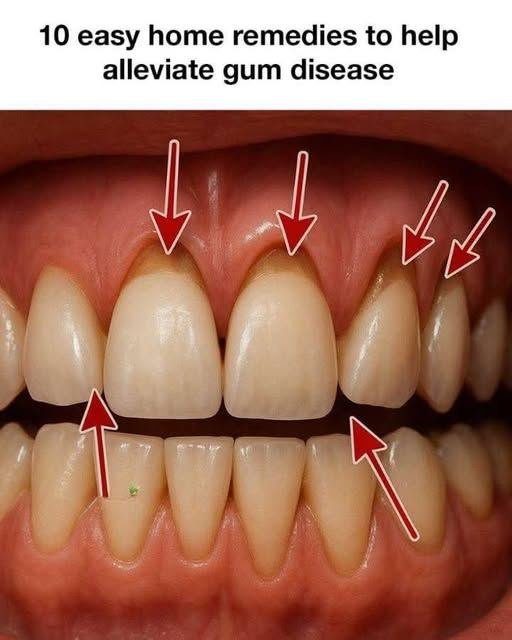
Gum disease, medically known as periodontal disease, is a widespread oral health problem that affects the gums and the tissues supporting the teeth. It begins with plaque, a sticky layer of bacteria that forms on teeth daily. Without proper brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into tartar, triggering gum irritation and infection.
Several factors increase the risk of developing gum disease. Smoking, hormonal changes, diabetes, reduced saliva flow from certain medications, and genetic predisposition all contribute. In its early stage, gingivitis, symptoms include redness, swelling, and bleeding gums. If ignored, it can progress to periodontitis, leading to bone damage and tooth loss.
Pages: 1 2


